Cross-border trade is expected to expand from $29 trillion in 2019 to almost $39 trillion by 2022, growing at a rapid rate. This growth is fueled by things like expansions in international trade, borderless e-commerce, consumer payments across borders, and web-based firms.
Global businesses are looking for solutions from their banks and fintech partners to make payments quicker, safer, and more transparent in order to satisfy this growing demand. Payment service providers are using technological advancements to improve the cross-border payments experience.
Cross-border payments involve currency transactions between individuals or businesses in different countries. The sender typically selects a front-end provider, such as a bank or a money transfer service like Western Union or Transferwise, to initiate the payment. The recipient receives the funds through the specified medium chosen by the sender.
Traditionally, cross-border payments have flowed through the correspondent banking network (CBN), which most front-end providers use for settlement. However, recent years have seen the emergence of new back-end networks aimed at optimizing cross-border payments, enabling interoperability between payment methods, and expanding sender-receiver possibilities.
Historically, banks dominated the cross-border payments market, led by a few global correspondent banks with limited competition. This arrangement resulted in challenges for both individuals and businesses, including a lack of transparency, lengthy settlement times, high transaction costs, and limited accessibility.
These issues were more pronounced in transactions involving less common currencies. For instance, sending money from a German local bank account to a bank account in Senegal could incur significant costs and take up to seven days to settle, with no confirmation of success.
This environment has attracted disruptors to the market, leading to increased competition and fragmentation as companies focus on different geographic areas, transaction sizes, and payment segments.
As a result of continued innovation, four crucial cross-border payment experiences are moving into the digital era.
JP Morgan details 4 ways digital innovation is transforming cross-border payments landscape
- APIs make real-time FX rates possible.
- APIs play a crucial role in enabling real-time foreign exchange (FX) rates for businesses.
- Treasury departments within global organizations seek digital solutions to optimize cross-currency workflows without disrupting their operations.
- APIs are plug-and-play solutions that seamlessly integrate into existing treasury infrastructure and interfaces.
- Treasurers benefit from APIs by gaining real-time visibility into FX rates directly from their existing systems.
- API integration helps treasurers effectively manage currency exposure, mitigate risk across global accounts, and accelerate reconciliation by providing early access to FX rates.
- Corporate treasurers can use API connectivity to lock in FX rates for predetermined time periods, allowing them to price their goods in favorable currencies while efficiently managing funds on the backend.
- Technology improves transparency and visibility
- Businesses have expanded access to diverse settlement mechanisms with global reach, allowing providers to offer payment options without complex technical overhead.
- Providers can collaborate with banks to utilize local clearing rails for cross-border payments, replacing traditional wire payments.
- The industry is progressing beyond traditional clearing rail advancements and adopting technologies such as SWIFT GPI, virtual account management, and API connectivity to enhance the payment exp,erience for both beneficiaries and senders.
- API connectivity benefits beneficiaries and senders by providing greater visibility and transparency regarding payment status.
- Senders can view FX rates upfront before initiating a payment.
- Beneficiaries can track payments in real-time and receive updates when issues arise during a payment.
- Implementation of these technologies enables beneficiaries and senders to better manage their cash positions across multiple bank accounts, enhancing predictability.
- Virtual accounts expand reach internationally
- Many businesses have direct deposit accounts (DDA) in countries where their beneficiaries are located, resulting in dispersed funds across various countries, accounts, and currencies.
- This dispersion can lead to complex reporting, idle cash balances, and unnecessary cross-currency risk exposure.
- Virtual account management solutions address these challenges by providing clients with a centralized account structure to manage cash flow across currencies.
- Businesses no longer need to maintain multiple local accounts in the same markets when using virtual accounts.
- Centralized account structures offer benefits such as improved payment sequencing and comprehensive reporting.
- Companies can easily transfer or concentrate balances from one account in one currency to another account in a different currency, or fund local payments using a centralized account.
- This approach helps businesses maximize liquidity, reduce risk exposure, and operate efficiently in the currencies that align with their business needs.
- The Growing Demand for Real-Time Cross-Border Payments and Blockchain’s Role
- The cross-currency, cross-border payments space is experiencing increasing demand for real-time payments.
- Globalized partnerships enable providers to offer senders multiple options for making real-time FX payments.
- Clients can now pay international customers and vendors instantly, reducing settlement periods and minimizing friction.
- Distributed ledger technology, commonly known as blockchain, is poised to revolutionize cross-border payments.
- Blockchain technology promises faster, cheaper, and more secure settlement of cross-border transactions.
- It streamlines processes like wire transfers and sanction screenings, significantly reducing clearance times.
- Blockchain also facilitates easier information sharing for international trade, enhancing payment visibility throughout the payments continuum.
The JP Morgan Prediction for cross-border payments
The future of cross-border payments is focused on making money movement faster, more secure, and transparent. This involves several key trends:
- Embedding Digital Innovation: The payment industry is integrating digital innovations into traditional clearing rails to enhance existing technologies.
- Creating New Solutions: Real-time payments and digital wallets are being developed as new solutions to improve cross-border transactions.
- Digital Trends Driving Change: Current digital trends are shaping the future of cross-border payments, with ongoing developments in technology and payment methods.
- Rise of Non-Bank Providers: The landscape is witnessing the emergence of non-bank payment providers offering innovative solutions.
Treasurers are urged to work with dependable partners that can provide all-encompassing connectivity solutions to handle this shift. By incorporating cross-currency solutions into current operations, our partnership will help firms stay up with global expansion and changing customer needs.
EY also identifies three of their own key trends which it believes are reshaping cross-border payments:
- Changing Consumer Demands: The cross-border payments market is evolving rapidly due to shifting consumer preferences. Consumers now expect banking services to be fast and user-friendly, and they are increasingly reluctant to pay for such services. The rise of smartphones and the popularity of alternative payment methods (APMs) for remittances have created new demands that traditional banks are struggling to meet. Alternative payment solution providers that offer quicker, more cost-effective, and transparent cross-border payment options can gain a competitive edge over traditional banks.
- Increasing Trade with Emerging Markets: Cross-border payments are experiencing a significant shift towards emerging markets in Africa, Latin America, and Asia. These regions are gaining a larger share of international transactions, driven by initiatives such as the African Continental Free Trade Area and China’s Belt and Road Initiative. Overall, global cross-border trade is projected to grow by approximately 5% (CAGR) between 2018 and 2022, with emerging markets showing even more substantial growth at around 11% (CAGR) during the same period. In contrast, protectionist policies in developed markets, such as Brexit and US trade tensions, are expected to slow down growth to around 2% (CAGR) between 2018 and 2022.
- Accessibility of Mobile Phones and E-Payments: The increasing ownership of mobile phones is expanding access to banking services and electronic payment solutions worldwide. In emerging economies, approximately 83% of adults own mobile phones, boosting financial inclusion. By 2017, 69% of the global population had a bank account and/or mobile wallet, up from 62% in 2014. This trend is expected to continue as mobile wallets are forecasted to experience significant growth. Global mobile wallet usage at the point of sale (POS) is expected to increase from around 22% in 2019 to approximately 30% in 2023, while mobile wallet usage in e-commerce is projected to grow to over half, reaching around 52% in 2023, up from roughly 42% in 2019. This growth in mobile payments is contributing to the expansion of cross-border commerce volumes.
Stripe, Visa, and Citi implementing cross-border payment solutions to address the growing demand
- Stripe: Stripe offers a cross-border payouts service that simplifies sending payments to individuals or businesses in different countries. It allows users to handle various currencies, payment methods, and compliance needs through a single integration, making cross-border payments faster and more cost-effective.
- Visa: Visa has partnered with Currencycloud to launch Visa Cross-Border Solutions. This service caters to banks, Fintechs, FX brokers, and other payment institutions, offering a suite of modular building blocks that can be integrated into existing technology infrastructure. It enables features like receiving payments in multiple currencies, real-time foreign exchange rates, and multi-currency wallets. Visa’s focus is on enhancing the end-user experience and collaborating with other divisions and customers to provide embedded multi-currency and cross-border functionality.
- Citi: Citi has released a report highlighting the substantial growth expected in cross-border payments. It emphasizes the opportunities presented by the increase in cross-border payment volumes, which are predicted to rise from $150 trillion in 2017 to over $250 trillion by 2027. Citi’s report discusses the evolving competition in the industry, the role of emerging technologies like digital assets and AI, and the importance of prioritizing client experience to deliver best-in-class cross-border payment services.
These major financial institutions and more are actively pursuing cross-border payment solutions to streamline transactions, lower expenses, and enhance the entire international payment experience for people, organizations, and businesses.
Market Appeal and Growth in Cross-Border Payments
The cross-border payment market’s substantial size makes it attractive to newcomers.
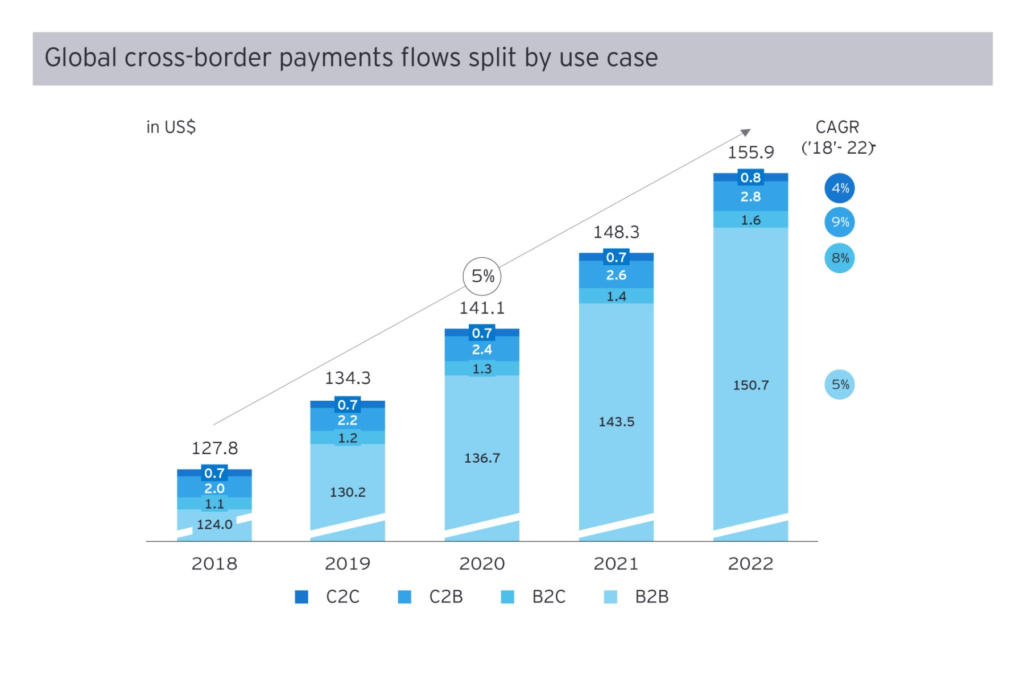
Global cross-border payment flow is growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 5% and is projected to exceed US$156 trillion by 2022.
The market breakdown includes:
- Business-to-Business (B2B) transactions, making up the largest share, are expected to reach US$150 trillion.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B) transactions, encompassing cross-border e-commerce and offline tourism spending, are forecasted to reach US$2.8 trillion.
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C) transactions, covering wage salaries and interest payments, are expected to total US$1.6 trillion in 2022.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) transactions, primarily remittances, contributed the least at an estimated US$0.8 trillion in 2022.
New entrants in the cross-border payments market are primarily focusing on low-value transactions within the C2C, B2C, and B2B segments.
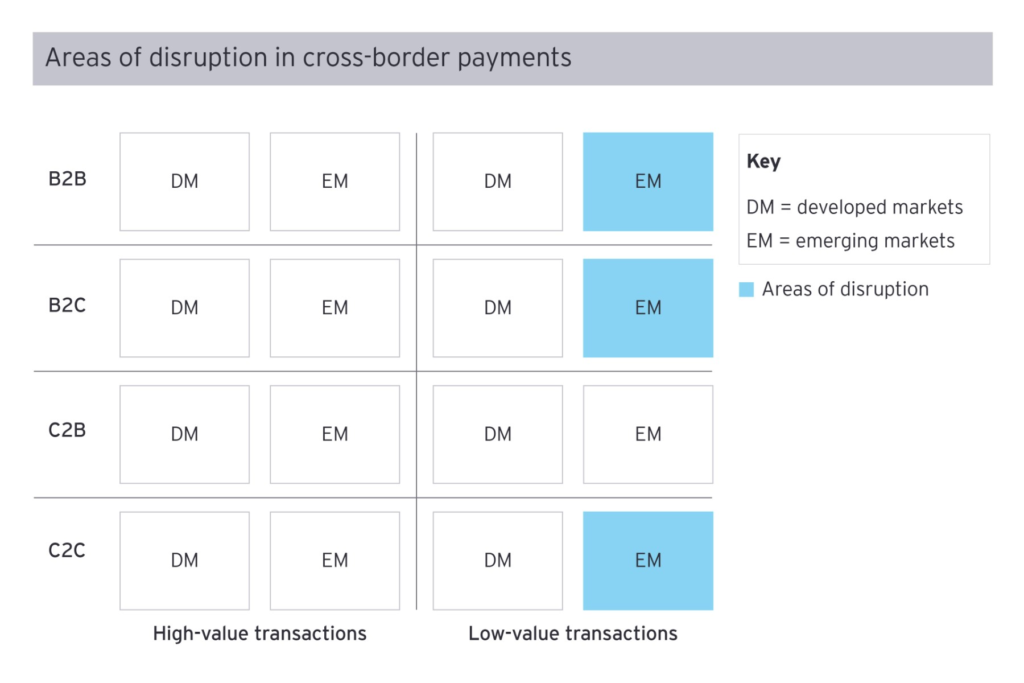

These segments are currently underserved by traditional banks and payment providers.
Low-value transactions in emerging markets are particularly disruptive due to changing consumer behaviour, increased trade with emerging markets, and improved financial inclusion efforts.

Final Thoughts
There are many different aspects to the environment of business-initiated international transfers. Banks are anticipated to continue to dominate these markets, and central bank networks (CBNs) are still effective and dependable in developed nations.
In emerging nations, the position is more complicated. Banks are expected to continue to dominate high-value transactions, but if working capital barriers can be removed, aggregators and money transfer operators (MTOs) could challenge them in low-value B2B transactions.
The independence of front-end players limits vertical integration and makes them undesirable acquisition candidates. Instead, we predict modest merger and acquisition (M&A) activity at the regional level in the consumer front-end market.
It will take a deliberate strategy grounded on in-depth local market and industry knowledge to navigate this complicated and diversified market.

